In today’s digital age, where our lives are increasingly intertwined with the internet, data privacy has become a critical concern. Lets explore the significance of data privacy and what practical steps to take on safeguarding your personal information online
Understanding Data Privacy
What is Data Privacy?
Data privacy refers to the proper handling, processing, and storage of personal information. It encompasses the rights of individuals to control how their data is collected, used, and shared. In the digital realm, this includes everything from your browsing history and social media activity to financial records and health information.
Personal data can be categorized into several types:
- Personally Identifiable Information (PII): This includes names, addresses, social security numbers, etc.
- Behavioral data: Information about your online activities, purchases, and preferences.
- Health data: Medical records, fitness tracker data, and other health-related information.
- Financial data: Bank account details, credit card information, and financial transactions.
- Biometric data: Fingerprints, facial recognition data, and other unique physical characteristics.
The Impact of Data Privacy
The consequences of poor data privacy practices can be far-reaching. According to a 2024 study by IBM, the average cost of a data breach reached $4.88 million per incident, a 10% rise from the previous year. Beyond financial implications, data breaches can lead to identity theft, reputational damage, and even personal safety risks.
Moreover, the societal impact of data privacy issues is profound:
- Erosion of trust in digital services and institutions
- Potential for discrimination based on collected data
- Chilling effect on freedom of expression due to fear of surveillance
- Manipulation of consumer behavior through targeted advertising
Data Privacy Laws and Regulations
Governments worldwide have recognized the importance of data privacy, leading to the implementation of various laws and regulations:
- General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR) in the European Union: Implemented in 2018, GDPR gives EU citizens more control over their personal data and imposes strict rules on those hosting and processing this data, anywhere in the world.
- California Consumer Privacy Act (CCPA) in the United States: Effective from 2020, CCPA enhances privacy rights and consumer protection for residents of California.
- Personal Information Protection and Electronic Documents Act (PIPEDA) in Canada: Governs how private sector organizations collect, use, and disclose personal information.
- Brazil’s General Data Protection Law (LGPD): Came into effect in 2020, closely mirroring GDPR.
- China’s Personal Information Protection Law (PIPL): Implemented in 2021, it’s one of the world’s strictest data privacy laws.

These regulations aim to give individuals more control over their personal data and hold organizations accountable for its protection. Key principles include:
- Consent: Organizations must obtain explicit consent before collecting personal data.
- Purpose limitation: Data should only be collected for specified, explicit, and legitimate purposes.
- Data minimization: Only necessary data should be collected and processed.
- Accuracy: Personal data must be kept accurate and up to date.
- Storage limitation: Data should not be kept longer than necessary.
- Integrity and confidentiality: Appropriate security measures must be in place to protect personal data.
Ensuring Data Privacy Online
Protecting Personal Information
To safeguard your data online, consider implementing these measures:
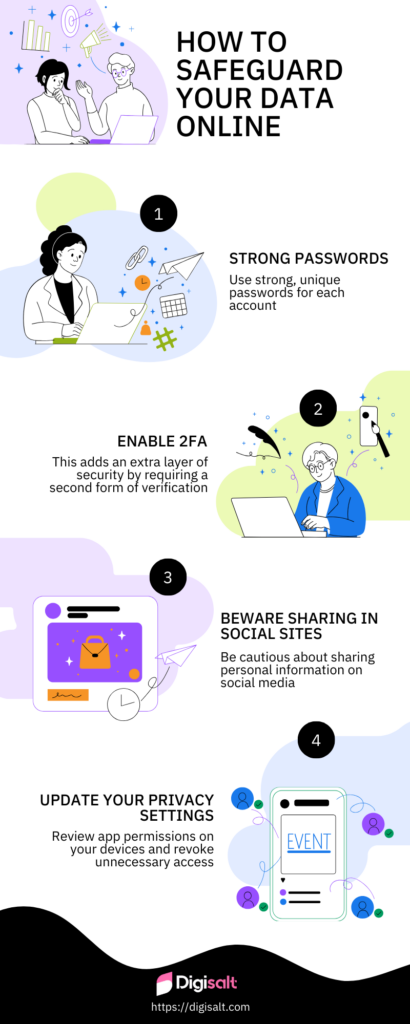
- Use strong, unique passwords for each account
- Use a combination of uppercase and lowercase letters, numbers, and symbols
- Aim for at least 12 characters in length
- Consider using a password manager to generate and store complex passwords securely
- Enable two-factor authentication (2FA) whenever possible
- This adds an extra layer of security by requiring a second form of verification
- Options include SMS codes, authenticator apps, or physical security keys
- Be cautious about sharing personal information on social media
- Regularly review and adjust your privacy settings
- Be mindful of the information you share in posts, photos, and profile details
- Regularly update your privacy settings on all platforms
- Social media platforms often change their privacy policies, so stay informed
- Review app permissions on your devices and revoke unnecessary access
Best Practices for Data Security
- Keep your software and operating systems up-to-date
- Enable automatic updates whenever possible
- Regularly check for and install updates on all your devices
- Use a reputable virtual private network (VPN) when accessing public Wi-Fi
- A VPN encrypts your internet traffic, making it harder for others to intercept
- Choose a VPN provider with a strong privacy policy and no-logs commitment
- Encrypt sensitive files and communications
- Use full-disk encryption on your devices
- Opt for end-to-end encrypted messaging apps for sensitive communications
- Regularly back up your data to a secure location
- Use the 3-2-1 backup rule: 3 copies, 2 different media types, 1 offsite
- Encrypt your backups to add an extra layer of protection
A 2022 survey by the Pew Research Center found that 79% of U.S. adults reported being somewhat or very concerned about how companies use the data they collect about them. This highlights the growing awareness of data privacy issues among the general public.
Risks of Ignoring Data Privacy
Neglecting data privacy can lead to severe consequences:
- Identity theft: In 2021, the FTC received 1.4 million reports of identity theft. This can result in financial loss, damaged credit scores, and countless hours spent trying to reclaim one’s identity.
- Financial loss: Cybercrime is projected to cost the world $10.5 trillion annually by 2025. This includes direct theft, fraud, embezzlement, and the costs associated with recovering from cyber attacks.
- Reputational damage: 81% of consumers said they would stop engaging with a brand online following a data breach. For individuals, privacy breaches can lead to embarrassment, loss of job opportunities, or damaged personal relationships.
- Surveillance and manipulation: Large-scale data collection enables detailed profiling, which can be used for targeted advertising, political manipulation, or even social control in some contexts.
- Discrimination: Data collected about individuals can be used to make decisions about employment, insurance, or credit, potentially leading to unfair treatment based on protected characteristics.

Data Privacy in Business
Importance of Data Privacy for Businesses
For businesses, maintaining robust data privacy practices is crucial for:
- Building customer trust: 87% of consumers say they would not do business with a company if they had concerns about its security practices.
- Complying with legal requirements: Non-compliance can result in hefty fines (e.g., up to €20 million or 4% of global turnover under GDPR)
- Protecting intellectual property: Data breaches can expose trade secrets and proprietary information
- Maintaining a competitive advantage: Strong privacy practices can differentiate a company in the market
Legal and Ethical Considerations
Companies must navigate a complex landscape of legal and ethical considerations when handling customer data. This includes:
- Obtaining explicit consent for data collection and use
- Implement clear, easy-to-understand privacy policies
- Use opt-in rather than opt-out mechanisms for data collection
- Implementing data minimization practices
- Only collect and retain data that is necessary for the stated purpose
- Regularly audit and delete unnecessary data
- Ensuring data accuracy and providing access to individuals
- Allow users to view, correct, and delete their personal data
- Implement processes to keep data up-to-date
- Reporting data breaches promptly
- Develop an incident response plan
- Comply with breach notification laws in relevant jurisdictions
The Future of Data Privacy
As technology continues to evolve, new challenges and opportunities in data privacy are emerging:
Artificial Intelligence and Machine Learning
- AI systems can process vast amounts of data, raising concerns about privacy and algorithmic bias
- Privacy-preserving AI techniques, such as federated learning, are being developed
Internet of Things (IoT)
- The proliferation of connected devices increases the attack surface for data breaches
- Implementing privacy by design in IoT devices is crucial
Blockchain and Decentralized Systems
- Blockchain technology offers new possibilities for user-controlled data and privacy-preserving transactions
- Challenges remain in balancing transparency with privacy
Quantum Computing
- Quantum computers could potentially break current encryption methods
- Development of quantum-resistant cryptography is underway
Privacy-Enhancing Technologies (PETs)
- Techniques like homomorphic encryption and zero-knowledge proofs are enabling data analysis without exposing raw data
As these technologies develop, it’s crucial for individuals, businesses, and policymakers to stay informed and adapt their privacy practices accordingly.
In conclusion, data privacy is not just a personal concern but a societal imperative. As we continue to live more of our lives online, it’s crucial that individuals and organizations alike prioritize the protection of personal information. By understanding the importance of data privacy, implementing best practices, and staying informed about emerging technologies and regulations, we can create a safer and more trustworthy digital environment for all.
Sources:
- IBM Cost of a Data Breach Report 2024
- Pew Research Center: “How Americans View Data Privacy” (2023)
- Federal Trade Commission Consumer Sentinel Network Data Book 2021
- Cybersecurity Ventures: “Cybercrime To Cost The World $10.5 Trillion Annually By 2025”
- KPMG: “Corporate Data Responsibility: Bridging the Consumer Trust Gap” (2021)

